SubNanosecond Arithmetic
SNAP: the Stanford Nanosecond Arithmetic Processor

This material is based upon work supported by the
National Science Foundation
under Grants No. MIP 88-22961 and 93-13701.
"Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations
expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not
necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation."
Objective:
- To develop high performance and most efficient arithmetic algorithms.
- To develop basic high performance technology.
Some Accomplishments:
- Addition in less than 1 nsec (1990)
[BSD88]
- Multiplication in less than 5 nsec (1993)
[Bewick94]
- Wave pipelined arithmetic units and vector processors
with 5x improved cycle times
[Nowka95]
- Floating Point Add
- Integrated rounding algorithm
[QuaFly92]
- Variable latency algorithm
[Oberman96]
- Floating Point Multiply
- Floating Point Divide
- New high radix algorithm
[WF92]
- SRT optimization
[Oberman96]
- Code reorder study
[26]
- Basic functions - Rapid approximations to basic functions
using partial product tree of a multiplier
[Schwarz93]
- FUPA - Floating point unit performance-area index
and application to state of the art.
[FQF95]

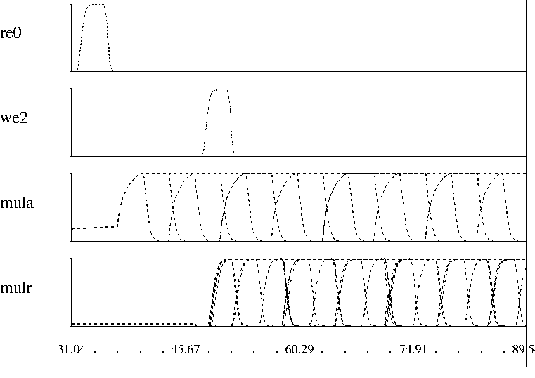
| 
|
| A 100Mhz multiplier clocked at 650Mhz using wave pipelining.
| A 16b piece of a multiplier (MAGIC layout) used in optimization study.
|

WEB-BASED TOOLS -
1.
FUPA tool, which predicts area and delay for particular floating
point unit implementations.
2.
Floating Point Divider Designer ,
which automatically generates the contents of
the central table for SRT division algorithms.

GROUP PUBLICATIONS
:
|
Books
|
Dissertations
|
Selected Papers
|
Technical Reports
|








